The Role of IoT in Modern CNC Systems
In the era of Industry 4.0, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems are evolving beyond automation. They are becoming interconnected, intelligent, and adaptive—thanks to the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT).
IoT enables CNC machines to collect and share real-time data, enhancing productivity, reducing downtime, and enabling predictive maintenance. This transformation marks a new phase in manufacturing where machines don’t just operate—they communicate, analyze, and optimize themselves.
This comprehensive guide walks through the step-by-step process of integrating IoT applications into CNC systems, offering insights on the hardware, data, platforms, and optimization techniques required for seamless connectivity.
1. Integration of IoT into CNC Systems: Key Steps
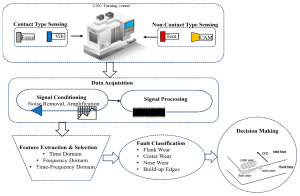
IoT allows CNC machines to exchange data continuously with other connected devices, tracking parameters such as machine status, power usage, temperature, and vibration. This data-driven infrastructure supports more flexible and responsive production.
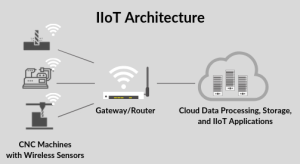
Step 1: Selection and Installation of IoT Hardware
Building an IoT-enabled CNC system starts with the right hardware foundation. Essential components include sensors, communication modules, and gateways.
Core Components:
- Sensors: Monitor temperature, vibration, pressure, speed, and energy consumption. These are the eyes and ears of the system, capturing live data from every machine.
- Network Modules: Facilitate connectivity via Wi-Fi, Ethernet, Bluetooth, or Zigbee for seamless communication.
- Gateway Devices: Connect older (legacy) CNC machines to IoT networks, bridging analog systems with digital platforms.
These devices form the backbone of machine-to-machine communication, enabling factories to gather actionable insights across the production floor.
Step 2: Establishing Data Collection and Processing Systems
Once the hardware is installed, CNC systems must process and interpret the data effectively. This requires robust data pipelines and processing platforms.
Key Components of Data Processing:
- Data Collection Software: Aggregates real-time information from sensors into a centralized database or cloud system.
- Processing Platforms: Cloud-based or on-premise platforms use analytics and AI algorithms to convert raw data into meaningful insights.
- Big Data Analytics: Large-scale data analysis identifies hidden patterns, inefficiencies, or failure trends.
This data-driven ecosystem ensures that decisions are based on facts, not assumptions, improving operational agility and responsiveness.
Step 3: Selecting and Integrating an IoT Platform
The IoT platform is the control center of the connected factory. It consolidates data, analyzes performance, and provides visualization tools for managers and operators.
Core Features to Consider:
- Advanced Analytics: Converts real-time machine data into reports that improve decision-making.
- Alerts and Notifications: Sends automated warnings when irregularities or performance drops are detected.
- User-Friendly Dashboards: Provide intuitive interfaces for monitoring machine status, energy usage, and maintenance needs.
The chosen platform should integrate smoothly with the factory’s existing IT infrastructure and CNC control systems.
2. Optimization of CNC Systems with IoT
Once IoT integration is complete, the focus shifts toward performance optimization—turning raw data into measurable improvements in efficiency, quality, and sustainability.
Step 4: Performance Monitoring and Optimization
IoT continuously tracks performance parameters such as speed, pressure, vibration, and temperature. Through this, manufacturers gain insights into machine health and production quality.
Performance Optimization Process:
- Continuous Data Monitoring: Sensors stream operational metrics in real time.
- Data Analysis: AI and ML models analyze deviations to identify inefficiencies or suboptimal settings.
- Optimization Algorithms: Automatically adjust machining parameters like cutting speed or feed rate to boost productivity.
For example, adjusting spindle speed based on real-time vibration data can prevent chatter, extend tool life, and improve surface finish—all without manual intervention.
Step 5: Predictive Maintenance and Fault Forecasting
Predictive maintenance is one of IoT’s most impactful benefits for CNC systems. It replaces reactive maintenance with data-driven foresight.
How It Works:
- Sensor-Based Monitoring: Sensors track wear, temperature, and vibration of machine components.
- Predictive Analytics: AI models use this data to forecast potential failures before they occur.
- Maintenance Scheduling: Maintenance activities are planned proactively, reducing unplanned downtime and maintenance costs.
Result: Machines stay operational longer, service costs decrease, and production remains consistent.
3. Benefits and Challenges of IoT in CNC Systems
While IoT brings enormous potential to CNC machining, it also introduces certain challenges that must be managed carefully.
Benefits
- Higher Efficiency: Real-time performance tracking optimizes production parameters.
- Reduced Downtime: Predictive maintenance minimizes machine failures.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Instant feedback empowers operators to make smarter, faster adjustments.
- Sustainability: Monitoring energy usage helps reduce waste and operational costs.
Challenges
- High Initial Investment: Setting up sensors, gateways, and software requires capital expenditure.
- Data Security: Connected devices create vulnerabilities that require advanced cybersecurity protocols.
- Data Management: Processing large data volumes demands scalable cloud or edge computing solutions.
Manufacturers that strategically plan for these challenges can unlock IoT’s full potential and gain a competitive edge.
Conclusion: Building the Smart Factory of the Future
IoT integration within CNC systems is not just a technical upgrade—it’s a strategic transformation. It allows machines to think, communicate, and evolve alongside production needs. By following a clear roadmap—selecting the right hardware, integrating intelligent platforms, and leveraging analytics—manufacturers can achieve significant improvements in efficiency, precision, and reliability.
At Radonix, with over 16 years of expertise in CNC control and automation, we help industries implement IoT solutions that bring intelligence and sustainability to every stage of machining. The future of manufacturing lies in connectivity—and IoT is the key to unlocking it.
Contact Us:
- E-Mail: info@radonix.com
- Phone: +90 (553) 920 5500