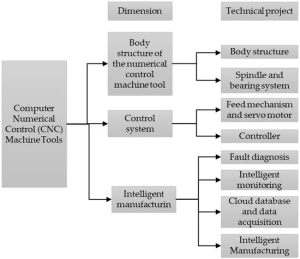
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) has transformed manufacturing—and it’s still evolving at speed. Today’s CNC software leverages the latest technologies to accelerate production, boost efficiency, and reduce errors across the shop floor.
This article examines the most current CNC software trends alongside future development directions, explaining how they impact real-world operations.
Together, these advances are shaping the industry’s next phase—opening the door to smarter, more efficient, and increasingly automated production processes.

Current CNC Software Trends
Driven by Industry 4.0, CNC software is evolving faster than ever.
Modern solutions go beyond basic machine control — they now optimize, monitor, and manage every stage of production.
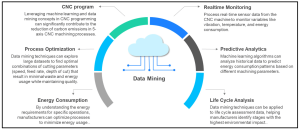
Key trends shaping today’s CNC software include cloud-based platforms, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and advanced simulation technologies.
Cloud-Based CNC Software Solutions
Cloud-based CNC software plays a critical role in modern manufacturing by centralizing data and enabling remote access.
These solutions store information on secure servers and allow operators to monitor and control production processes from anywhere with an internet connection. Beyond accessibility, cloud-based platforms deliver major advantages in performance optimization and cost savings.
-
Data Access and Sharing: Centralized data management ensures information from multiple CNC machines is instantly available, improving collaboration and decision-making.
-
Flexibility and Scalability: As production demands increase, cloud systems can be scaled effortlessly, allowing manufacturers to expand operations without infrastructure bottlenecks.
-
Cost Efficiency: Because updates and maintenance are handled on the server side, businesses save on IT resources while keeping their systems up to date.
AI and ML-Driven CNC Programming
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming CNC software by making machining processes smarter and more adaptive. By analyzing historical production data, these technologies identify patterns, optimize workflows, and enhance decision-making in real time.
-
Data Analysis and Optimization: AI-driven algorithms review past production data to refine toolpaths and G-codes, reducing cycle times and minimizing material waste.
-
Fault Detection and Automatic Correction: Continuous monitoring allows AI to detect anomalies instantly and recommend corrective actions, preventing costly errors.
-
Smarter Decision Making: ML models improve over time by learning from previous machining runs, enabling faster setups, higher efficiency, and more consistent part quality.
Simulation and Digital Twin Technology
Simulation software enables CNC machines to be tested in a virtual environment, detecting potential errors before they occur on the shop floor.
By combining simulation with digital twin technology, manufacturers gain a powerful tool to optimize precision and reduce risks.
-
Toolpath Optimization: Simulation software tests toolpaths in advance, identifying potential errors and suggesting more efficient machining routes.
-
Digital Twin Technology: Digital twins create real-time virtual models of CNC machines, simulating their behavior and performance. This allows manufacturers to test and fine-tune processes before actual production.
-
Time and Cost Savings: Detecting and correcting issues during simulation significantly reduces production errors, minimizes material waste, and lowers operational costs.
Future CNC Software: New Trends and Perspectives
Looking ahead, CNC software will become more autonomous, intelligent, and interconnected.
Advancements in Industry 4.0, artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and robotics will continue to transform CNC systems into highly adaptive smart manufacturing solutions.
Automatic Program Generation and AI Integration
AI-driven software will further automate the programming process by analyzing part geometry and generating optimized G-codes and machining strategies.
-
Automatic Code Generation: AI automatically interprets workpiece features, creates toolpaths, and converts them into optimized G-codes.
-
Data Analytics and Continuous Improvement: AI algorithms continuously learn from past machining operations, refining efficiency, accuracy, and process reliability over time.
Autonomous CNC Systems and Smart Manufacturing
The next generation of CNC machines is moving toward fully autonomous production. These systems are capable of starting and completing machining operations without human intervention, using sensors and advanced data analytics to optimize each step.
- Autonomous Machine Operations
Autonomous CNC machines, connected with sensors and powered by AI, can independently manage the entire production cycle. They analyze data in real time, adjust parameters automatically, and continuously optimize performance for higher efficiency.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Intervention
Through IoT connectivity, these machines are constantly monitored. If a malfunction occurs, the system instantly detects the issue and suggests corrective actions. This real-time intervention ensures minimal downtime, improved reliability, and consistent production quality.
Asset Management and Predictive Maintenance
CNC machine maintenance is becoming smarter and more proactive with the adoption of predictive maintenance technologies.
Instead of waiting for breakdowns, manufacturers can anticipate and prevent issues before they occur.
-
IoT-Supported Asset Management: IoT devices continuously monitor machine status and collect real-time data. This information helps forecast performance and identify future maintenance needs.
-
Machine Learning for Predictive Maintenance: AI-driven algorithms analyze machine data to predict failures in advance, enabling timely, proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
VR and AR-Supported CNC Training
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are transforming CNC machine training, offering safe and interactive learning environments.
-
CNC Training Simulations: VR simulations allow operators to practice machining processes in a risk-free digital environment, reducing errors on real machines.
-
On-Site AR Support: With AR, operators receive real-time guidance during live operations, improving accuracy and minimizing mistakes.
Conclusion
CNC software continues to evolve, paving the way for faster, safer, and more efficient manufacturing processes.
From AI-powered predictive maintenance to VR training, and from cloud-based solutions to digital twin technologies, the future of CNC software is driven by automation and intelligence.
By embracing these innovations, manufacturers can boost efficiency, reduce costs, minimize human error, and stay competitive in the rapidly advancing world of smart manufacturing.
Contact Us:
- E-Mail: info@radonix.com
- Phone: +90 (553) 920 5500