Navigating CNC Control Panel Functions efficiently can shave minutes off every setup, reduce errors, and boost operator confidence.
In this 2025-ready, step-by-step guide, we break down the essential CNC Control Panel Functions—from axis jogging and zero return to program management, diagnostics, and safety interlocks—so operators, trainers, and maintenance teams can master the control panel of cnc machine workflows quickly and safely.
You’ll learn standard sequences, common pitfalls, and customization tips that translate across brands, plus Radonix-specific notes for clean integration.
We’ll also cover modern enhancements like voice-activated controls, predictive analytics dashboards, and modular interfaces that simplify multi-machine oversight.
For foundational context on motion planning and controller architecture, see the Radonix blog primer: How CNC Controller Works: Full Guide to Precision Control.
Overview of CNC Control Panel Functions in Modern Machines
A modern cnc machine control panel is a unified interface combining HMI screens, hard keys, and safety devices, backed by a PLC and the CNC kernel.
Together, they orchestrate motion, execute programs, monitor I/O, and surface alarms in real time.
What’s inside the ecosystem
- HMI screens for program edit, offsets, tool tables, and live diagnostics.
- Hard keys for cycle start/hold, emergency stop, jog, and overrides.
- PLC-backed safety and sequencing for interlocks, guards, and lubrication.
- Fieldbus diagnostics for drives, I/O blocks, and probes.
- Optional add-ons: MPG handwheels, barcode/QR scanners, and touchscreen control panel kits.
Evolution at a glance
- Analog to digital: From discrete lamps and relays to configurable HMIs with role-based dashboards.
- Paper to data: From printed work instructions to in-panel SOPs, live KPIs, and alarm histories.
- Standalone to connected: CNC controllers now stream telemetry for predictive maintenance and cross-machine analytics.
Core CNC Control Panel Functions for Daily Operations
At the heart of productive days are predictable routines. The following CNC Control Panel Functions streamline start-up, jogging, and homing while preventing avoidable mistakes.
Step-by-Step Breakdown: Axis Control and Jogging Functions
Power-on sequence
- Turn on main disconnect and control power; verify HMI boots and safety circuits are healthy.
- Confirm emergency stop is released and doors/interlocks are closed.
Manual jogging
- Select axis (X/Y/Z/A/B) with a dedicated switch or on-screen selector.
- Choose jog mode: continuous or incremental (x1, x10, x100).
- Use jog keys or MPG handwheel for fine positioning near set-up points.
Zero return (homing)
- Ensure fixtures/tools are clear; press Home/Zero Return.
- Observe homing messages; confirm repeatability and axis coordinates reset.
Set work offset and tool length
- Use probe routines or feeler gauges; write values to G54–G59 and tool table entries.
- Lock offsets to reduce accidental edits.
Dry run and feed/speed override
- Use Dry Run mode if available; keep overrides visible, with max limits set by Admin.
Table: Axis functions—steps and common errors on the control panel of cnc machine
| Function | Steps | Common Errors |
| Power-On Check | E-stop released → Interlocks OK → Control power on | Skipped interlock check causes startup alarms |
| Manual Jog | Select axis → Mode (cont/inc) → Jog keys/MPG | Wrong axis selected; excessive jog speed near fixtures |
| Zero Return | Clear path → Press Home → Verify coordinates | Homing with clamps in path; ignoring homing error messages |
| Set Work Offset | Probe or touch-off → Write G54–G59 → Verify | Mixing inch/mm; writing to wrong WCS |
| Tool Length Set | Probe or touch setter → Update tool table | Wrong tool number; forgetting to commit changes |
| Dry Run | Activate dry run → Slow feed override → Simulate | Not elevating Z; skipping coolant and chip checks |
| Overrides | Adjust feed/spindle → Observe on HMI | Leaving overrides at 120% into next job |
Pro tip: Place modal indicators (units, WCS, plane) at the top of the HMI at all times. Many CNC Control Panel Functions fail simply because a mode was not visible.For a design deep dive, see: What Is a CNC Control Panel? Complete Guide 2025.
Program Management Functions in CNC Control Panels
Editing, loading, simulating, and verifying programs are core CNC Control Panel Functions. Standardizing these steps reduces scrap and accelerates first-article validation.
Step-by-step: Load, preview, and verify a job
Load program
- Insert USB/network path → Open Program Manager → Import file.
- The panel should show checksum/date; lock “last known good” versions for traceability.
Preview and simulate
- Open graphical preview → Verify stock, coordinate system, and tool list.
- Run backplot; check for rapids near clamps and correct G02/G03 plane.
Map resources
- Cross-check required tools and offsets with the machine’s tool table.
- Confirm coolant, probing macros, and subprogram calls are available.
Set run conditions
- Confirm units (G20/G21), WCS (G54–G59), and safe-start line.
- Set conservative feed/spindle overrides for first run.
Dry run and single-block
- Run Single Block for first 20–30 lines; verify real motion matches preview.
- Switch to continuous with modest feed override once safe.
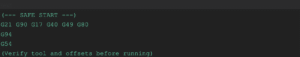
Code snippet: Safe-start template to paste into programs
Operator interface functions that help
- Contextual help: Tap line numbers to see active modes and offsets.
- Change tracking: The HMI logs program edits and tool table changes by user.
- Filters and search: Quickly find subprograms or M-codes across large jobs.
Interactive simulation tips
- Use “ghost stock” overlays in the preview to spot over-travel.
- Toggle display of machine envelope and fixture models.
- Enable collision check where supported; otherwise simulate at high Z for the first pass.
Diagnostic and Alarm Functions: Proactive Troubleshooting
Great CNC Control Panel Functions make troubleshooting fast and factual. The goal is to get from alarm to cause to fix in minutes, not hours.
What every panel should provide
- Alarm severity levels with plain-language descriptions.
- One-click access to likely causes, I/O states, and drive faults.
- Following error plots and axis scopes for motion diagnostics.
- Fieldbus topology pages (EtherCAT/Profinet) with node health.
Top 10 alarm patterns and quick actions
- E-stop engaged: Check mushroom switch, safety relay status.
- Door interlock: Verify magnetic sensors and alignment.
- Overtravel: Clear axes; check soft limits and re-home.
- Encoder fault: Inspect cable/shield; reseat connectors.
- Drive fault (overcurrent/overheat): Cool-down; check load and parameters.
- Following error exceeded: Lower feed; re-tune gains; check mechanics.
- Spindle orientation error: Recalibrate orientation; inspect encoder.
- Probe trigger during move: Verify probe status; disable when not in use.
- Network node lost: Check fieldbus cabling/IDs; power-cycle I/O block.
- Coolant/air pressure low: Inspect pump/valve; confirm sensors.
Table: Alarm diagnostics cheat sheet
| Alarm | What it means | Quick actions | Prevention |
| E-Stop Active | Safety chain open | Reset E-stop; check safety relay | Test at shift start; maintain switches |
| Axis Overtravel | Hit limit or soft limit | Clear axis; re-home; adjust soft limits | Validate WCS and tool lengths |
| Encoder Error | Feedback signal lost/noisy | Reseat cables; check shield/ground | Use shielded pairs; avoid power routing |
| Drive Overcurrent | Excess load/params | Reduce accel/jerk; inspect mechanics | Tune gains; maintain guides/lube |
| Following Error | Position lag too high | Lower feed; tune P/D; notch filters | Periodic ballbar; monitor FE trends |
Case study: 40% downtime reduction with Radonix panels
- Problem: A mid-size fab shop experienced recurring drive faults and slow recoveries across mixed-brand machines.
- Action: Standardized on Radonix CNC control panels with unified alarm taxonomy, QR-linked SOPs, and auto-captured context (tool, WCS, override states).
- Result: Mean time to recovery dropped 40%; training time for new hires fell by half thanks to consistent CNC Control Panel Functions.
Safety and Customization Functions for CNC Panels
Safety and usability go hand-in-hand. CNC Control Panel Functions should make safe choices easy and risky states obvious.
Safety functions you should enforce
- Dual-channel emergency stop with monitored relays.
- Door interlocks with status indicators on the HMI.
- Safe speed and safe stop (SS1/SS2) where supported by drives and PLC.
- Lockout/Tagout prompts for maintenance tasks.
Customization steps: Tailor the cnc machine control panel to your workflow
Define roles
- Operator, Setup, Maintenance, Admin with escalating permissions.
- Lock critical parameters; enable only task-relevant screens.
Arrange dashboards
- Pin “Offsets,” “I/O Monitor,” and “Alarm History” for Setup role.
- Collapse rarely used pages; reduce cognitive load.
Create macro buttons
- Safe Resume, Probe Corner, Coolant Purge, and Safe Retract.
- Map to hard keys or prominent soft buttons.
Standardize themes
- High-contrast theme for bright shops; large touch targets for gloves.
Audit and iterate
- Review alarm stats monthly; adjust dashboards to surface the most-used operator interface functions.
2025 Enhancements: Smart Functions in CNC Control Panels
Modern CNC Control Panel Functions are smarter, safer, and more connected.What’s new and practical
- Voice-activated functions
- “Show Offsets,” “Pause Cycle,” or “Start Probe Routine,” with confirmation prompts and role checks.
- Predictive analytics dashboards
- Real-time following error, spindle load, temperature trends, and anomaly alerts across multiple machines.
- Modular multi-machine interfaces
- Oversee several cells from one station; tile live status cards and jump into any HMI with one tap.
- AR-assisted troubleshooting
- Tablet or headset overlays guide where to check sensors/cables; QR codes deep-link from the HMI to AR steps.
Conclusion: Train the Motions, Standardize the Screens, Win the Day
Mastering CNC Control Panel Functions is the fastest way to cut setup time, avoid alarms, and keep parts moving. Standardize your power-up, jogging, zero return, and program verification routines; leverage diagnostics and guided fixes; and configure dashboards that surface the right operator interface functions at the right time. Whether you run legacy equipment or Radonix CNC control panels, consistent use of CNC Control Panel Functions delivers safer, faster, and more predictable results.Download our full panel quick-start and configuration checklist from the Radonix blog, and standardize across your fleet for maximum impact.Master these CNC control panel functions—get started with Radonix at radonix.com
FAQ
Q1: What are essential CNC Control Panel Functions?
A: Cycle start/hold, emergency stop, axis jogging, zero return, program load/preview, offsets/tool tables, alarms, and overrides. Modern CNC Control Panel Functions also include voice commands, predictive dashboards, and AR-assisted help.
Q2: How should I train operators on the control panel of cnc machine?
A: Teach a repeatable flow: power-up checks, home axes, set offsets, run dry simulation, then single-block. Use checklists and simulations on the cnc machine control panel to reinforce safe habits and reduce ramp-up time.
Q3: How do I troubleshoot recurring alarms faster?
A: Use the alarm center to view severity, likely causes, and I/O states. Follow guided fix macros and log events. Standardized CNC Control Panel Functions and Radonix panels’ QR-linked SOPs cut recovery time dramatically.
Q4: Can I customize dashboards on Radonix CNC control panels?
A: Yes. Rearrange widgets, pin macro buttons (safe resume, probing), set role-based permissions, and choose high-contrast themes. These CNC Control Panel Functions reduce clutter and focus operators on critical tasks.
Q5: Do voice commands work in noisy shops?
A: With confirmation prompts and quality microphones, yes. Limit voice to low-risk actions like “show offsets” or “open alarms.” Voice-enabled CNC Control Panel Functions speed navigation without risking unintended moves.
Q6: How do CNC controllers integrate with predictive analytics?
A: Radonix panels stream telemetry (following error, spindle load, temperatures) to dashboards that flag anomalies. These CNC Control Panel Functions enable proactive maintenance and minimize unplanned downtime.
Contact Us:
- E-Mail: info@radonix.com
- Phone: +90 (553) 920 5500