A poorly designed CNC Machine Control Panel can lead to 20% more operator errors and costly downtime. In 2025, the panel is more than buttons and a screen—it’s the command center that unites ergonomics, clear HMI logic, and robust hardware to keep parts flowing. This guide shows how to design and run a CNC Machine Control Panel that’s safer, faster, and easier to learn, using proven layout patterns and operation routines.
We’ll cover layout fundamentals, material and component choices, core cnc control panel functions, and day-to-day operating best practices. You’ll see how Radonix CNC control panels integrate with modern controllers for intuitive navigation, plus 2025 upgrades like touchless navigation, AR-assisted troubleshooting, and customizable dashboards. For foundational context on controls, start with How CNC Controller Works: Full Guide to Precision Control on the Radonix blog.
Fundamentals of CNC Machine Control Panel Design
Designing a CNC Machine Control Panel starts with the operator: eyesight, reach, gloves, and workflow. An ergonomic CNC panel boosts speed, reduces fatigue, and lowers error rates—especially during setup, probing, and recovery after alarms.Key principles
- Ergonomics and reach
- Mount the primary display around eye height, angle 10–20° to reduce glare.
- Place emergency stop and feed/spindle overrides within a 500–700 mm reach envelope.
- Clear HMI layout
- Cluster navigation, cycle start/hold, and jog controls logically; make “stop” larger and tactile.
- Use consistent iconography, high-contrast themes, and large touch targets for touchscreen CNC controls.
- Durable materials and protection
- Use IP54–IP65 enclosures, anti-glare toughened glass, and sealed keypads for coolants and chips.
- Integration with controllers
- Ensure panel wiring and I/O map match the chosen cnc controller types (e.g., PLC-based CNC panels).
- Provide panel space for future options: probes, automation, or extra axis jog dials.
- Safety first
- Redundant E-stops, compliant interlocks, and lockout/tagout points aligned with OSHA 1910.147.
Table: Design checklist for a CNC Machine Control Panel
| Area | Guideline | Measurement/Spec | Why it matters | Example |
| Display | Eye-level with tilt | Center ~1,500 mm from floor | Reduces neck strain | 15–19” industrial touchscreen |
| E-stop | Prominent, guarded | 40–45 mm mushroom, SIL-rated | Fast, reliable stop | Dual-channel safety relay |
| Jog controls | Tactile and grouped | Dedicated axes with selector | Prevents mis-jogs | Rotary selector + MPG handwheel |
| Overrides | Large knobs | 0–150% feed/spindle | Quick, precise control | Detent knobs, glove-friendly |
| Enclosure | IP-rated, shielded | IP54–IP65 | Coolant/chip resistance | Powder-coated steel, EMI gasket |
| HMI theme | High contrast | 6–8 mm min font height | Readability in glare | Dark theme with color-safe alarms |
| I/O labeling | Clear and durable | UV-stable tags | Faster service | Laser-etched markers |
Tip: When specifying a CNC Machine Control Panel for a retrofit, mock up cardboard layouts to validate reach and sight lines with real operators before buying hardware.
Core Functions of the CNC Machine Control Panel
The control panel of cnc machine workflows must make common tasks effortless and rare tasks discoverable. Good cnc control panel functions cut learning time and make recovery from mistakes far less stressful.Table: Functions, descriptions, and best-practice examples
| Function | Description | Best Practice Example |
| Cycle Start / Feed Hold | Launch or pause execution | Oversized, color-coded buttons; hold pauses both motion and coolant to assess chips |
| Emergency Stop | Immediate machine stop | Guarded E-stop, dual-channel SIL; test at shift start |
| Axis Jogging | Incremental/manual motion | MPG handwheel with axis selector and step size (x1, x10, x100) |
| Program Load/Select | Choose and preview jobs | Thumbnail preview, file checksum, and last-run parameters |
| Offsets and Tool Tables | Set work and tool data | Guided wizards for G54–G59, probing macros integrated |
| Alarm/Message Center | Show errors/warnings | Color-coded severities, one-click help link/QR to fix steps |
| Overrides | Feed, rapid, spindle | Detented knobs with on-screen readout and limits |
| I/O Monitor | Live signals view | Filter by PLC rung; color/animation when state changes |
| Fieldbus Diagnostics | Drive/network status | EtherCAT/Profinet topology view, node health indicators |
| Maintenance Panels | Timers, lubrication, filters | Countdown timers and checklist confirmations |
| User Roles | Access control | Operator/Setup/Admin profiles; lock critical parameters |
Best practices
- Use modal indicators (units, plane, coordinate system) always-on at the HMI top bar.
- Provide “what changed?” overlays after alarm recovery so operators see if offsets or overrides differ from standard.
- In a Fanuc control panel or similar, standardize soft-key paging so “Offsets,” “Program,” and “Alarms” occupy consistent positions across machines.
Best Practices for Operating CNC Machine Control Panels
Operations excellence is repeatable. These steps help operators bring up the machine, navigate confidently, respond to alarms, and hand off between shifts without surprises.
Daily startup routine
- Visual check: doors, guards, coolant, chip tray.
- Power sequence: main breaker, controller, drives; verify the CNC Machine Control Panel indicators.
- Home the machine; verify probe and tool magazine status.
- Load the day’s program and confirm correct work offset and tool table.
- Run a warmup cycle for spindle and axes.
HMI navigation tips
- Use favorites: bookmark offsets, alarm history, and I/O monitor—the most-used cnc control panel functions.
- Keep overlays minimal during cycle; show only feed/spindle overrides and part count to reduce distraction.
- Confirm units (G20/G21) and active WCS before pressing cycle start; consider a pre-start checklist prompt on the HMI.
Error and alarm handling
- Pause with Feed Hold, then open the alarm panel.
- Follow the guided “cause/fix” steps; if the control panel of cnc machine provides QR/Help, scan it.
- After clearing, run a “safe resume” macro to lift Z, re-approach at reduced feed, and re-enter the path.
- Log the event with short notes; these help cnc panel troubleshooting later.
Shift handoff
- Record overrides left active, tool wear edits, and pending maintenance.
- Use the panel’s digital handoff checklist to prevent missed steps.
Case study: Small shop, big gains
- Situation: A 12-person job shop struggled with inconsistent setups and frequent “wrong offset” alarms.
- Action: They standardized a CNC Machine Control Panel layout on three mills using Radonix CNC control panels, added a pre-start checklist, and mapped a “safe resume” button on the HMI. They also improved the offsets screen with larger fonts and color-coded active WCS.
- Result: 15% reduction in downtime, 12% fewer scrap parts over eight weeks, and faster cross-training for new operators.
Advanced Design: HMI for Manufactured Devices in CNC
Good HMI is product design. In 2025, hmi design for manufactured devices means responsive UI components, role-based views, and smart help baked into the workflow.Design patterns that scale
- Role-based dashboards: Operator sees cycle, overrides, and part count; Setup sees offsets, probe routines, and jog.
- Contextual help: Tap an alarm to see common causes, sensor/I-O states, and recovery macros.
- Visual standards: Use consistent typography, icon packs, and color semantics for “Run/Pause/Alarm.”
- Voice and touchless: Optional voice commands for hands-busy tasks (e.g., “show offsets”), with confirmation prompts.
Troubleshooting flows (flowchart description)
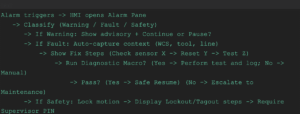
This structured cnc panel troubleshooting flow reduces guesswork. Two mentions of cnc panel troubleshooting are intentional here to align with search terms and practical usage.Customization ideas
- Theming and layout: Offer “high-contrast” and “bright shop” themes.
- Macro buttons: Let users pin their three most-used actions (probe corner, safe resume, coolant purge).
- Analytics widget: Live following error or spindle load chart to catch issues early in the cycle.
2025 Innovations in CNC Control Panel Design and Operation
Panel tech is evolving fast. Here’s what’s practical in 2025—and worth adopting.
- Touchless interfaces
- Gesture and proximity sensors navigate common screens without direct contact—useful with gloves and oily environments.
- Voice shortcuts with confirmation prevent accidental actions; ideal for touchscreen CNC controls where tapping is imprecise with gloves.
- AR overlays for troubleshooting
- Tablet or headset overlays show live sensor states and “point-here” instructions on the machine enclosure.
- QR codes on the CNC Machine Control Panel link to AR-guided procedures.
- AI-driven diagnostics
- The panel correlates alarms, I/O transitions, and drive data to recommend likely fixes.
- Predictive warnings appear on the dashboard before faults cascade.
- Modular, scalable hardware
- Radonix CNC control panels support plug-in MPG modules, extra hard keys, and expansion bays for future axes—ideal for PLC-based CNC panels or mixed fleets with a Fanuc control panel on legacy machines.
Conclusion: Design Well, Operate Better, and Scale with Confidence
A well-designed CNC Machine Control Panel pays for itself through fewer mistakes, faster setups, and happier operators. Combine smart ergonomics with a clear HMI, standardize daily routines, and leverage modern features like AI diagnostics and AR help. Whether you run a Fanuc control panel, Siemens-based system, or Radonix CNC control panels, the principles hold.When you’re ready to standardize panels across your fleet and integrate with advanced controllers, Radonix can help you deliver a safer, more productive control experience.Implement these CNC machine control panel best practices—discover Radonix panels at radonix.com
FAQ
Q1: What are key cnc control panel functions?
A: Core functions include cycle start/hold, emergency stop, axis jogging, program load/preview, offsets and tool tables, and an alarm center with diagnostics. The CNC Machine Control Panel should keep modal indicators visible and provide role-based views for operators, setup, and maintenance.
Q2: How do I design the control panel of cnc machine for ergonomics?
A: Keep the display near eye height, group jog controls with clear axis selection, and use large, tactile E-stops and override knobs. Choose IP-rated enclosures and anti-glare glass. Pilot the layout with operators to validate reach and visibility on your CNC Machine Control Panel before purchase.
Q3: How can I speed up training on a new panel?
A: Standardize HMI layouts across machines, use consistent iconography, and enable on-screen tooltips. Provide a pre-start checklist and a “safe resume” macro. A consistent CNC Machine Control Panel reduces context switching and shortens the learning curve for cross-trained staff.
Q4: What’s the role of PLC in panel behavior?
A: PLC logic manages interlocks, sequences, and safety chains behind the HMI. PLC-based CNC panels let you expose key rung states in the diagnostics screen, improving cnc panel troubleshooting and making alarm causes visible without opening the cabinet.
Q5: Do touchscreens replace hard keys?
A: Not entirely. Touchscreen CNC controls are great for navigation and previews, but hard keys excel for critical actions in gloves and under stress (E-stop, feed hold, jog). A hybrid CNC Machine Control Panel offers the best reliability and usability.
Q6: Can AR and AI really help on the shop floor?
A: Yes. AR overlays show where to check sensors or valves right on the machine, and AI correlates alarms and I/O to suggest fixes. Together they speed cnc panel troubleshooting and reduce restarts, especially helpful for newer operators on complex jobs.








