Industry 5.0 and CNC Technologies: New Horizons in Human-Machine Collaboration
Industry 5.0 marks a new era where human creativity and machine intelligence merge to achieve smarter, more sustainable, and more ethical manufacturing. While Industry 4.0 focused on automation and digitalization, Industry 5.0 emphasizes collaboration between humans and advanced technologies.
Among these technologies, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems play a crucial role, transforming from mechanical tools into intelligent, collaborative partners that amplify human capability.
This article explores how Industry 5.0 is reshaping CNC technologies, enhancing efficiency, flexibility, and sustainability, while redefining the relationship between humans and machines.
1. Philosophical Foundations and Technological Trends of Industry 5.0
Industry 5.0 is built on the concept of human-machine collaboration, extending the digitalization and automation-driven structure of Industry 4.0. This new industrial paradigm integrates technology with human creativity and ethical values, while prioritizing social responsibility and environmental sustainability.
1.1 The Symbiotic Relationship between Humans and Technology
Industry 5.0 aims not only to alleviate the workload of machines but also to facilitate the collaboration between human intelligence and creativity. This symbiotic relationship is based on three key philosophies:
- Human-Centered Design:
- Technologies are designed to optimize user experience.
- For example, advanced human-machine interfaces (HMIs) used in CNC machines allow operators to manage complex processes more intuitively.
- Ergonomics and user-friendly interfaces reduce physical and mental strain on machine operators.
- Social Responsibility:
- Industry 5.0 encourages making ethical decisions in manufacturing processes and minimizing environmental impacts.
- Solutions in CNC machines that reduce energy consumption support environmental sustainability by lowering carbon emissions.
- Flexible Manufacturing:
- Flexible production lines are created to meet individual consumer demands.
- Multi-axis machining technologies in CNC machines allow the realization of various product designs on the same production line.

1.2 Technological Tools and Approaches
Industry 5.0 humanizes production processes powered by advanced technologies. This transformation in CNC technologies occurs through the following innovations:
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots):
- Cobots that can work in the same environment as humans are integrated into CNC machines, helping operators avoid repetitive tasks.
- Cobots enhance the efficiency of CNC machines in processes such as material handling, loading/unloading, and quality control.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
- AI algorithms are used for data analysis and predictive maintenance in CNC machines.
- For instance, AI algorithms can detect tool wear during CNC machining and provide real-time intervention recommendations.
- Digital Twin Technology:
- Digital replicas of CNC machines are created in the digital environment.
- This technology allows monitoring machine performance, optimizing machining strategies, and detecting potential errors before they occur.
- Advanced Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs):
- Touchscreens, augmented reality (AR), and voice commands enrich interfaces, making it easier and more efficient for CNC operators to control machines.
- HMI systems allow operators to adjust machining parameters in real-time and easily diagnose complex faults.
2. Industry 5.0 Applications in CNC Technologies
CNC machines, with the integration of Industry 5.0, are equipped with innovative applications that increase flexibility, efficiency, and human-machine compatibility.
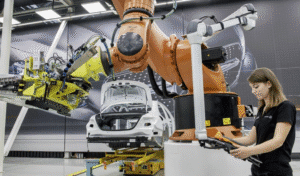
2.1 Cobot Integration and Human-Machine Collaboration
The integration of cobots into CNC machines enhances both the speed and safety of production processes. This collaboration makes the manufacturing environment more efficient and safer.
Example Applications:
- Automatic Material Loading and Unloading:
- Cobots transport workpieces to CNC machines, minimizing errors caused by manual operations.
- Particularly in precision manufacturing processes, the use of cobots prevents damage to workpieces.
- Assembly and Quality Control:
- During the measurement and inspection processes of finished parts, cobots equipped with laser scanners or cameras reduce the rate of defective products.
- For instance, cobots can transport parts from the CNC machine to measurement stations for automatic measurement and reporting.
- Cellular Manufacturing Systems:
- Manufacturing cells where cobots and CNC machines work together create flexible and modular production lines.
- For example, a cobot can transfer a part from one CNC machine to the next machine for further processing.
2.2 AI-Enabled CNC Technologies
Artificial intelligence has become a fundamental element in making CNC technologies smarter and more efficient, bringing the vision of Industry 5.0 to life.
AI-Driven Innovations:
- Process Optimization:
- AI optimizes cutting speeds, feed rates, and chip removal strategies, reducing processing time and energy consumption.
- For example, AI-enabled CNC machines can automatically create optimal toolpaths for complex geometries.
- Predictive Maintenance:
- Data from CNC machine sensors is analyzed by AI algorithms to predict potential failures.
- This prevents unplanned downtime and ensures uninterrupted production processes.
- Error Prevention and Quality Assurance:
- AI monitors CNC machine operations in real time to detect potential errors in advance.
- For example, vibrations or tool wear occurring during machining can be immediately reported by AI systems.
2.3 Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI) and Operator Experience
Modern HMI systems in CNC machines are equipped with innovations that reflect the human-centered approach of Industry 5.0.
Advantages of HMI Systems:
- Intuitive Control Panels:
- Touchscreens and graphical user interfaces enable operators to manage machines more quickly and easily.
- Operators can monitor and modify all machining parameters in real-time through a single screen.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
- AR technology facilitates CNC machine maintenance and setup processes.
- Operators can use VR headsets to inspect digital models of CNC machines and test machining strategies beforehand.
- Error-Tolerant Systems:
- HMI systems include suggestion mechanisms and automatic correction tools that reduce operator errors.
- For example, if an incorrect machining parameter is entered, the system automatically offers an alternative suggestion or takes safety precautions.
As a result, the adaptation of CNC technologies to Industry 5.0 strengthens human-machine collaboration, making manufacturing processes more flexible, efficient, and user-friendly. These systems will continue to shape the production paradigms of the future.
3. Hybrid Manufacturing and the Future of CNC Technologies
Hybrid manufacturing, which combines CNC processes with additive manufacturing (3D printing) technologies, represents an innovative approach that pushes the boundaries of traditional manufacturing processes. These systems address complex manufacturing needs while optimizing material use and supporting environmental sustainability.
3.1 Advantages of Hybrid Systems
Hybrid manufacturing systems combine the strengths of both additive and subtractive manufacturing technologies. The key advantages of these systems include:
- Production of Complex Geometries:
- Additive manufacturing allows the creation of complex geometries, such as hollow structures, mesh-like patterns, or internal channel systems, which are impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
- CNC processes allow for precise finishing and surface quality enhancement of these structures.
- Material Efficiency:
- The additive manufacturing process uses only the required amount of material, minimizing waste.
- CNC processes remove unwanted protrusions or excess material to create the final form of the product.
- Design and Prototyping Processes:
- Rapid prototyping allows early detection of design flaws and reduces the time to market.
- Prototypes produced with hybrid systems and CNC processes have the required precision and durability for functional testing.
- Multi-Material Manufacturing:
- Hybrid systems allow different materials to be combined within a single product. For example, a part may be made from titanium for its durability, while another section is made from plastic for lightness.
3.2 Future Potentials
Hybrid manufacturing systems have the potential to transform manufacturing technologies in the future. Significant advancements are expected in the following areas:
- Nano and Micro-Scale Manufacturing:
- The high precision capabilities of CNC machines, when combined with hybrid systems, enable manufacturing at micro and nano scales.
- This technology can be used for producing microscopic implants in the medical sector or microchip components in the electronics industry.
- Autonomous Manufacturing Cells:
- The integration of AI, cobots, and hybrid manufacturing systems could lead to fully autonomous production lines.
- These cells could perform material feeding, production, and quality control processes without human intervention.
- Industrial Customization:
- The production of fully personalized products based on consumer demands will become more common.
- For example, customized prosthetics and implants tailored to the anatomical features of each individual can be quickly produced with hybrid systems.
- Use in Space and Aerospace:
- Hybrid systems are critical for producing complex and lightweight components for spacecraft.
- In-situ manufacturing capabilities enable hybrid systems to produce replacement parts during space missions when needed.
4. Sustainability and Environmental Impact
One of the main goals of Industry 5.0 is to transform manufacturing processes according to the principles of environmental sustainability. CNC technologies are equipped with innovations that contribute to this objective.
4.1 Circular Economy Approach
Circular economy aims to reduce waste and make production processes sustainable by reusing materials. CNC machines offer significant advantages in this context:
- Recyclable Chip Materials:
- Metal, plastic, or composite materials that result as chips in CNC machines can be recycled and reintroduced into the production process.
- For example, aluminum chips can be melted down and used as raw material again.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Modern CNC machines use servo motors and intelligent energy management systems to optimize energy consumption.
- Regenerative braking systems recover excess energy generated by the machines, reducing total energy usage.
4.2 Carbon Footprint Reduction
Among the environmental goals of Industry 5.0 is minimizing carbon emissions. CNC machines are equipped with various technological innovations to help achieve this objective:
- Green Manufacturing Technologies:
- CNC machines are being designed to run on renewable energy sources. For example, manufacturing facilities powered by solar or wind energy are rapidly becoming more common.
- Sustainable Cooling Systems:
- Environmentally friendly coolants used in CNC machines more effectively manage heat generated during production.
- These coolants are less toxic and biodegradable compared to traditional cooling oils.
- Technology to Reduce Material Waste:
- CNC machines apply minimal chip removal techniques during machining, reducing raw material waste.
- These technologies offer significant savings in high-cost materials used in industries like aerospace and automotive.
5. Conclusion: The Future of CNC Technologies and Industry 5.0
Industry 5.0 is a transformation process that makes manufacturing processes more human- and environmentally-friendly. CNC technologies play a key role in this transformation:
- Human-Centered Approach:
- Machines that support human creative potential make work processes both easier and more efficient.
- Technological Advancement:
- Artificial intelligence, cobots, and hybrid manufacturing systems have made CNC machines smarter, more flexible, and more autonomous.
- Environmental Responsibility:
- CNC technologies have become pioneers in achieving sustainability goals, such as energy efficiency, reducing material waste, and promoting recyclable manufacturing.
In conclusion, the synergy between CNC technologies and Industry 5.0 will establish the foundation for future manufacturing processes, not only economically but also ethically. This combination promises to shape industrial development while re-establishing the balance between humanity and nature.
Contact Us:
- E-Mail: info@radonix.com
- Phone: +90 (553) 920 5500